Change in Net Working Capital NWC Explained
It is an indicator of operating cash flow, and it is recorded on the statement of cash flows. And the cash flow is one of the important factors to be considered when we value a company. It indicates whether the short-term assets increase or decrease concerning the short-term liabilities from one year to the next.
- Understanding changes in cash flow is also important if you are applying for a small business loan.
- The essence of the concept is that if a company has a positive working capital, it means they have funds in surplus.
- For example, during the COVID-19 crisis, many companies shifted their focus to very practical measures, like days of cash on hand, as opposed to traditional performance metrics like revenue and EBITDA.
- Working capital is calculated by taking a company’s current assets and deducting current liabilities.
Leveraging Positive Net Working Capital

Alternatively, bigger retail companies interacting with numerous customers daily, can generate change in net working capital cash flow short-term funds quickly and often need lower working capital. Improving efficiency may require investment in better technology, upgrading machinery, or training employees. By reinvesting wisely, the company can maintain its competitive edge and position itself for future success.
Net Working Capital Formula
- If current liabilities is increasing, less cash is being used as the company is stretching out payments or getting money upfront before the service is provided.
- The balance sheet organizes assets and liabilities in order of liquidity (i.e. current vs long-term), making it easy to identify and calculate working capital (current assets less current liabilities).
- A company’s balance sheet contains all working capital components, though it may not need all the elements discussed below.
- As it so happens, most current assets and liabilities are related to operating activities (inventory, accounts receivable, accounts payable, accrued expenses, etc.).
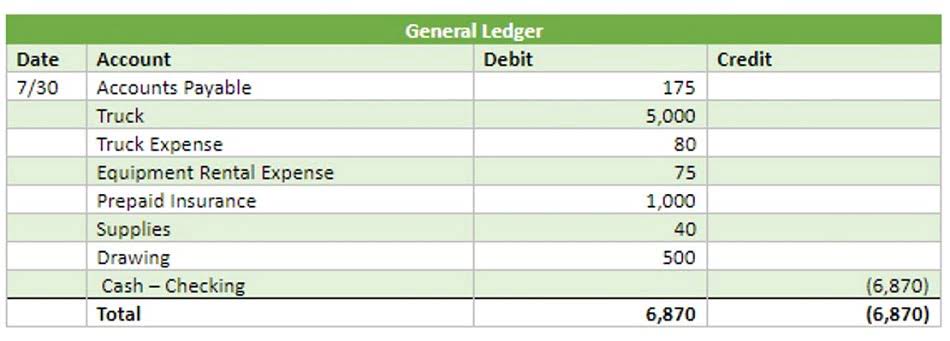
- Change in Working capital cash flow means an actual change in value year over year, i.e., the change in current assets minus the change in current liabilities.
Still, it’s important to look at the types of assets and liabilities and the company’s industry and business stage to get a more complete picture of its finances. Therefore, as of March 2024, Microsoft’s working capital metric was approximately $28.5 billion. If Microsoft were to liquidate all short-term assets and extinguish all short-term debts, it would have almost $30 billion remaining cash.
What is Working Capital? Formula, Meaning, Types, and Examples
Generally, companies like Walmart, which have to maintain a large inventory, have negative working capital. The essence of the concept is that if a company has a positive working capital, it means they have funds in surplus. The inverse of having a negative working capital indicates that the company owes more than it has in its cash flow. Companies can forecast future working capital by predicting sales, manufacturing, and operations. Forecasting helps estimate how these elements will impact current assets and liabilities. For what are retained earnings example, if a company has $100,000 in current assets and $30,000 in current liabilities, it has $70,000 of working capital.
- Until the payment is fulfilled, the cash remains in the possession of the company, hence the increase in liquidity.
- This is the complete guide to understanding net working capital, calculating changes in working capital, and applying this to calculating Warren Buffett’s version of free cash flow, Owner Earnings.
- As a business owner, it’s important to calculate working capital and changes in working capital from one accounting period to another to clearly assess your company’s operational efficiency.
- Unlike other measures that are used to analyze cash flow in a company, such as earnings or net income, free cash flow is a measure of profitability that excludes the non-cash expenses of the income statement.
- Changes in working capital reflect the fluctuations in a company’s short-term assets and liabilities over a specific period.
It’s not to see whether there are more current assets than current liabilities. If you are a business owner, it makes no sense to constantly check whether you have more assets than liabilities on the balance sheet. Looking at FCF is also helpful for potential shareholders or lenders who want to evaluate how likely it is that the company will be able to pay its expected dividends or interest. If the company’s debt payments are deducted from free cash flow to the firm (FCFF), a lender would have a better idea of the quality of cash flows available for paying additional debt.










